Few-shot prompting is the most effective middle ground between zero-shot instructions and full model fine-tuning, allowing you to guide AI behavior with just 2-5 carefully chosen examples. This technique dramatically improves output quality without requiring technical expertise or large datasets.
What Makes Few-Shot Prompting Work?
Few-shot prompting leverages in-context learning, where the model learns directly from examples in your prompt rather than relying solely on pre-trained knowledge. By showing multiple input-output pairs that follow your desired pattern, the model can quickly recognize what you want and apply that understanding to new inputs.
Unlike other approaches, few-shot prompting:
Requires no coding or model training
Works immediately with any capable language model
Adapts to your specific needs through example selection
Produces more consistent, predictable outputs
Types of Few-Shot Prompting
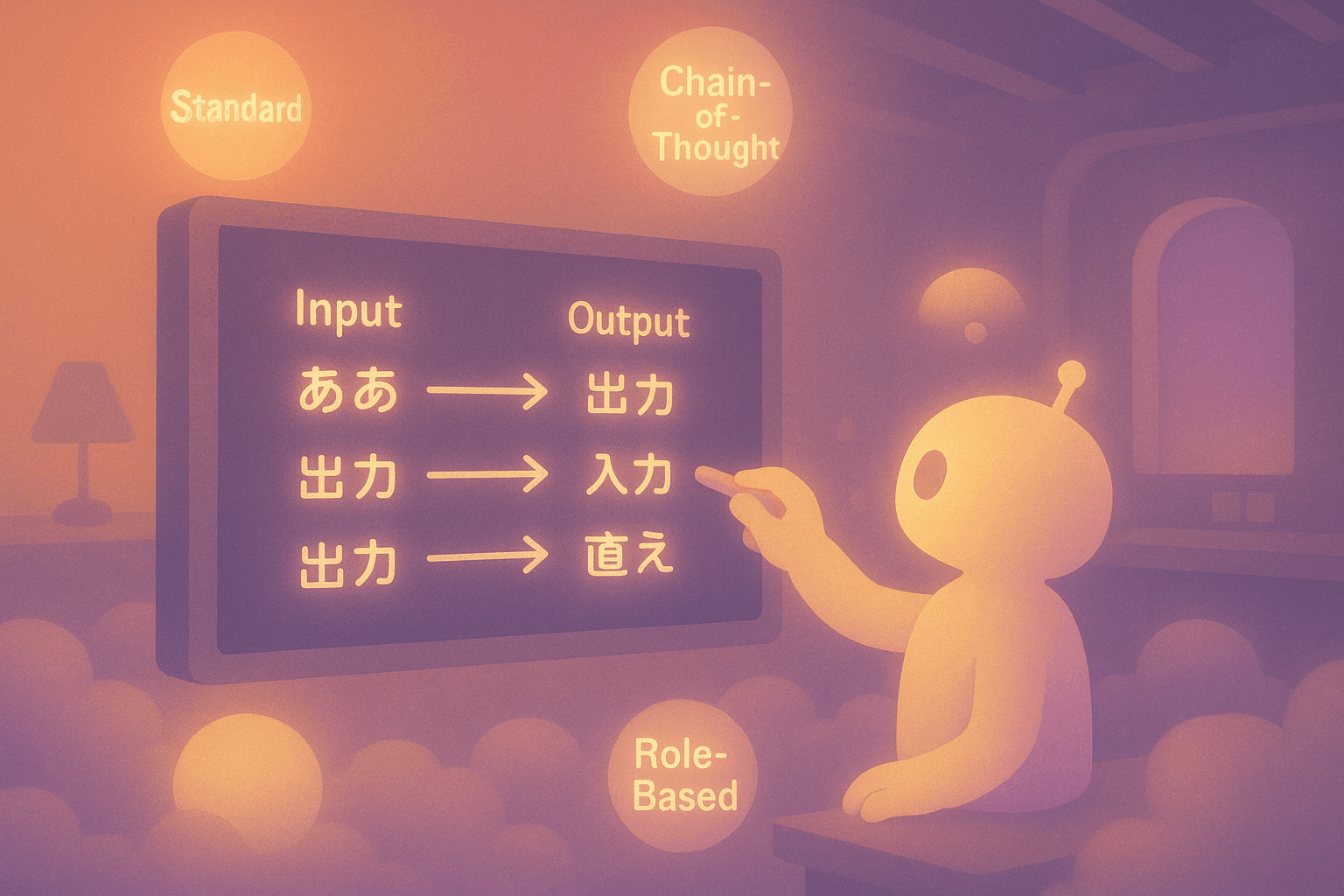
Standard Few-Shot: The basic approach where you provide several straightforward examples of inputs and outputs.
Chain-of-Thought Few-Shot: Examples include step-by-step reasoning to guide the model's thought process through complex problems.
Tree-of-Thought Few-Shot: Examples demonstrate branching reasoning paths, particularly useful for decision-making tasks.
Role-Based Few-Shot: Examples show the model adopting a specific persona or role to influence tone and style.
When to Use Few-Shot Prompting
When you need structured, formatted outputs
For complex classification or nuanced tasks
When training data is scarce or fine-tuning isn't practical
To control style, tone, or persona in generated text
For tasks requiring multi-step reasoning
Best Practices for Effective Few-Shot Prompts
Select relevant examples: Choose examples that closely match your target task to avoid confusing the model. As IBM explains, relevant examples help the model understand context more effectively.
Maintain consistent format: Keep all examples structured identically so the pattern is clear to the model.
Use diverse examples: Include variations covering different aspects of your task to improve the model's ability to generalize.
Keep examples concise: Avoid overly complex or ambiguous examples that might mislead the model.
Limit example quantity: Too many examples can overwhelm the model; LearnPrompting.org recommends 2-5 well-chosen examples for optimal results.
Provide clear instructions: Combine your examples with explicit task descriptions to set expectations.
Iterate and test: Experiment with different examples and prompt designs, evaluating outputs to refine your approach.
Practical Example: Sentiment Analysis
Here's a simple few-shot prompt for sentiment classification:
Classify the sentiment of the following texts as Positive or Negative.
Text: The product is terrible. Sentiment: Negative
Text: Super helpful, worth it. Sentiment: Positive
Text: It doesn't work! Sentiment:
The model, seeing these patterns, will likely classify the final example as "Negative" because it has learned the expected format and pattern recognition from your examples.
Why Few-Shot Works Better Than Alternatives
According to DigitalOcean's research, few-shot prompting significantly outperforms zero-shot prompting (giving instructions without examples) for complex tasks. It provides the context and pattern recognition the model needs without requiring the technical expertise of fine-tuning.
Few-shot prompting is especially valuable when you need to quickly adapt AI models to specific use cases or when you want to maintain flexibility in how tasks are performed.
Next Steps for Implementing Few-Shot Prompting
Identify tasks where your current prompts produce inconsistent results
Create 2-5 clear examples showing the exact input-output pattern you want
Test different example variations to see which produces the best results
Combine your examples with clear instructions for optimal performance
Want to streamline your AI workflows without the hassle of writing perfect prompts every time?
it's like having a personal assistant who handles the technical aspects of AI automation. Just describe what you want to automate, and Wordware creates reliable, consistent workflows that save you time and effort. No coding required. Automate repetitive tasks and focus on what truly matters in your work.